Using a timer interrupt allow any task to become active at any specific time. It makes the main program loop to do other tasks without waiting. SysTick is a timer bases on interrupt inside the STM32 ARM micro-controller.
 |
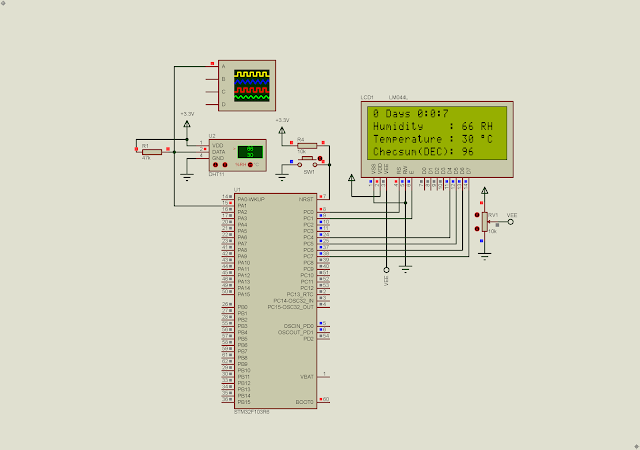
| Simulating Program In Proteus |
In this introductory example, I use this time to toggle an LED. LED blinking is placed inside the SysTick function. It left the main program loop blank. We can place any task inside the main program loop, for example a button pressing event.
 |
Code Configuration Wizard |
Code configuration wizard allow the programmer to generate code by selecting and setting any features of the STM32 micro-controller. In this example, I select PC0 as an digital output connects to the LED. Its core source codes are generated by IOC.
The SysTick interrupt occurs for every 100us. Click here to download its source file.
For other similar posts please check,
- Getting Started With STM32F103C8T6 Module with STM32CubeIDE
- STM32F103C8T6 Blue Pill SysTick and Multiplexing Display Example
- STM32F103C8T6 Blue Pill Switch And Multiplexing Display Interface Using SysTick
- STM32F103C8T6 Blue Pill SysTick LED Blinking
- STM32F103R6 Common Anode Seven Segments Display Example
- STM32F103R6 Common Anode Seven Segments Display And Switch Interfacing
- STM32F103R6 Simple 2-Digit Multiplexing Display And Switch Example
- STM32F103R6 SysTick And Digital Clock Example
- STM32F103R6 SysTick Two-Digit Multiplexing Display and Push Button
- LED Blinking With STM32F103R6 Using SysTick
- STM32F103R6 SPI Interfaces To SN74HC595N Shift Registers



No comments:
Post a Comment